Configuration¶
Directory Layout¶
Elassandra merges the Cassandra and Elasticsearch directories as follows :
conf: Cassandra configuration directory + elasticsearch.yml default configuration file.bin: Cassandra scripts + elasticsearch plugin script.lib: Cassandra and elasticsearch jar dependencypylib: Cqlsh python library.tools: Cassandra tools.plugins: Elasticsearch plugins installation directory.modules: Elasticsearch modules directory.work: Elasticsearch working directory.
Elasticsearch paths are set according to the following environment variables and system properties:
path.home: CASSANDRA_HOME environment variable, cassandra.home system property, the current directory.path.conf: CASSANDRA_CONF environment variable, path.conf or path.home.path.data: cassandra.storagedir/data/elasticsearch.data, path.data system property or path.home/data/elasticsearch.data
Configuration files¶
Elasticsearch configuration relies on Cassandra configuration file conf/cassandra.yaml for the following parameters.
| Cassandra | Elasticsearch | Description |
|---|---|---|
cluster.name |
cluster_name |
Elasticsearch cluster name is mapped to the cassandra cluster name. |
rpc_address |
network.host |
Elasticsearch network.host is set to the cassandra rpc_address. |
broadcast_rpc_address |
network.publish_host |
Elasticsearch network.publish_host is set to the cassandra broadcast_rpc_address. |
listen_address |
transport.host |
Elasticsearch transport_host is set to the cassandra listen_address. |
broadcast_address |
transport.publish_host |
Elasticsearch transport.publish_host is set to the cassandra broadcast_address. |
Node role (master, primary, and data) is automatically set by Elassandra, standard configuration should only set cluster_name, rpc_address in the conf/cassandra.yaml.
By default, Elasticsearch HTTP is bound to the Cassandra RPC address rpc_address, while Elasticsearch transport protocol is bound to the Cassandra internal address listen_address.
You can overload these default settings by defining Elasticsearch network settings in conf/elasticsearch.yaml (in order to bind Elasticsearch transport on
another interface).
By default, Elasticsearch transport publish address is the Cassandra broadcast address. However, in some network configurations (including multi-cloud deployment), the Cassandra broadcast address is a public address managed by a firewall, and
it would involve network overhead for Elasticsearch inter-node communication. In such a case, you can set the system property es.use_internal_address=true to use the Cassandra listen_address as the Elasticsearch transport published address.
Caution
If you use the GossipingPropertyFile Snitch to configure your cassandra datacenter and rack properties in conf/cassandra-rackdc.properties, keep in mind that this snitch falls back to the PropertyFileSnitch when gossip is not enabled. So, when re-starting the first node, dead nodes can appear in the default DC and rack configured in conf/cassandra-topology.properties. It will also breaks the replica placement strategy and the computation of the Elasticsearch routing tables. So it is strongly recommended to set the same default rack and datacenter for both the conf/cassandra-topology.properties and the conf/cassandra-rackdc.properties.
Logging configuration¶
The Cassandra logs in logs/system.log includes elasticsearch logs according to your conf/logback.conf settings.
See cassandra logging configuration.
Per keyspace (or per table) logging level can be configured using the logger name org.elassandra.index.ExtendedElasticSecondaryIndex.<keyspace>.<table>.
Multi datacenter configuration¶
By default, all Elassandra datacenters share the same Elasticsearch cluster name and mapping. This mapping is stored in the elastic_admin keyspace.
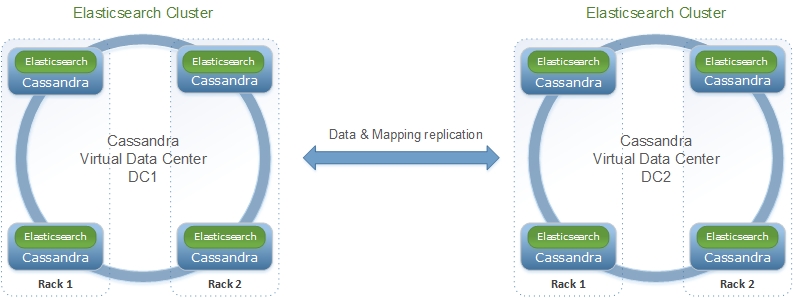
If you want to manage various Elasticsearch clusters within a Cassandra cluster (when indexing different tables in different datacenters), you need to set a datacenter.group in conf/elasticsearch.yml and thus, all elassandra datacenters sharing the same datacenter group name will share the same mapping.
These elasticsearch clusters will be named <cluster_name>@<datacenter.group> and mappings will be stored in a dedicated keyspace.table elastic_admin_<datacenter.group>.metadata.
All elastic_admin[_<datacenter.group>] keyspaces are configured with NetworkReplicationStrategy (see data replication).
where the replication factor is automatically set to the number of nodes in each datacenter. It ensures maximum availibility for the elaticsearch metadata. When removing a node from an elassandra datacenter, you should manually decrease the elastic_admin[_<datacenter.group>] replication factor in accordance with the number of nodes.
When a mapping change occurs, Elassandra updates the Elasticsearch metadata in elastic_admin[_<datacenter.group>].metadata within a lightweight transaction to avoid conflict with concurrent updates.
This transaction requires QUORUM available nodes that are more than half the nodes of one or more datacenters regarding your datacenter.group configuration.
It also involves cross-datacenter network latency for each mapping update.
Caution
Elassandra cannot start Elasticsearch shards when the underlying keyspace is not replicated on the datacenter the node belongs to.
In such case, the Elasticsearch shards remain UNASSIGNED and indices are red. You can fix that by manually altering the keyspace replication map,
or use the Elassandra index.replication setting to properly configure it when creating the index.
Tip
Cassandra cross-datacenter writes are not sent directly to each replica. Instead, they are sent to a single replica with a parameter telling to the replica to forward to the other replicas in that datacenter. These replicas will directly respond to the original coordinator. It reduces network traffic between datacenters when there are replicas.
Elassandra Settings¶
Most of the settings can be set at various levels :
- As a system property, default property is es.<property_name>
- At cluster level, default setting is cluster.default_<property_name>
- At index level, setting is index.<property_name>
- At table level, setting is configured as a _meta:{ “<property_name> : <value> } for a document type.
For example, drop_on_delete_index can be :
- set as a system property
es.drop_on_delete_indexfor all created indices. - set at cluster level with the
cluster.default_drop_on_delete_indexdynamic settings, - set at index level with the
index.drop_on_delete_indexdynamic index settings, - set as an Elasticsearch document type level with
_meta : { "drop_on_delete_index":true }in the document type mapping.
Dynamic settings are only relevant for clusters, indexes and document type setting levels, system settings defined by a JVM property are immutable.
Sizing and tuning¶
Basically, Elassandra requires much CPU than the standalone Cassandra or Elasticsearch and Elassandra write throughput should be half the Cassandra write throughput if you index all columns. If you only index a subset of co lumns, write performance would be better.
Design recommendations :
- Increase number of Elassandra node or use partitioned index to keep shards size below 50Gb.
- Avoid huge wide rows, write-lock on a wide row can dramatically affect write performance.
- Choose the right Cassandra compaction strategy to fit your workload (See this blog post by Justin Cameron)
System recommendations :
- Turn swapping off.
- Configure less than half the total memory of your server and up to 30.5Gb. Minimum recommended DRAM for production deployments is 32Gb. If you are not aggregating on text fields, you can probably use less memory to improve file system cache used by Doc Values (See this excelent blog post by Chris Earle).
- Set -Xms to the same value as -Xmx.
- Ensure JNA and jemalloc are correctly installed and enabled.
Write performance¶
- By default, Elasticsearch analyzes the input data of all fields in a special _all field. If you don’t need it, disable it.
- By default, Elasticsearch indexes all fields names in a special _field_names field. If you don’t need it, disable it (elasticsearch-hadoop requires _field_names to be enabled).
- By default, Elasticsearch shards are refreshed every second, making new document visible for search within a second. If you don’t need it, increase the refresh interval to more than a second, or even turn if off temporarily by setting the refresh interval to -1.
- Use the optimized version less Lucene engine (the default) to reduce index size.
- Disable
index_on_compaction(Default is false) to avoid the Lucene segments merge overhead when compacting SSTables. - Index partitioning may increase write throughput by writing to several Elasticsearch indexes in parallel, but choose an efficient partition function implementation. For example, String.format() is much more faster that Message.format().
Search performance¶
- Use 16 to 64 vnodes per node to reduce the complexity of the token_ranges filter.
- Use the RandomSearchStrategy and increase the Cassandra Replication Factor to reduce the number of nodes requires for a search request.
- Enable the
token_ranges_bitset_cache. This cache compute the token ranges filter once per Lucene segment. Check the token range bitset cache statistics to ensure this caching is efficient. - Enable Cassandra row caching to reduce the overhead introduce by fetching the requested fields from the underlying Cassandra table.
- Enable Cassandra off-heap row caching in your Cassandra configuration.
- When possible, reduce the number of Lucene segments by forcing a merge.